What are fibroids?
Fibroids are abnormal growths that form in or on the uterus of a woman. These tumours can grow to be quite large, causing severe stomach pain and heavy periods. Call and book your appointment with Dr. Amita, the best gynae for women-uterine fibroids. In some circumstances, fibroids produce no visible indications or symptoms at all. Typically, the growths are benign, or noncancerous. Fibroids have an unknown cause.
What are the many forms of fibroids?
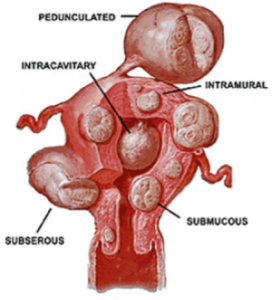
The type of fibroid that a woman develops is determined by its location within or on the uterus.
Fibroids in the intramural space – The most prevalent type of fibroid is intramural fibroids. These appear within the uterine muscle wall. Intramural fibroids can grow in size and strain your womb.
Fibroids in the subserosa – Subserosal fibroids develop on the outside of your uterus, known as the serosa. They may grow large enough to make one side of your womb appear larger than the other.
Pedunculated fibroids – Subserosal tumours can form a stem, which is a thin basis that supports the tumour. When this happens, they are referred to as pedunculated fibroids.
Fibroids in the submucosa – These tumours form in the uterus’s middle muscular layer, known as the myometrium. Submucosal tumours are less prevalent than the others.
Diagnosis of Fibroids
If your doctor feels your uterus during a regular pelvic exam, he or she may point out the possibility of you having uterine fibroids. If your uterus appears to be irregular or particularly huge, they may schedule more tests, such as an ultrasound. In an ultrasound pictures of your uterus are taken by using sound waves. To obtain the photos, a technician will insert a device into your vagina or onto your abdomen. Then your doctor can determine whether or not you have fibroids as well as where and how large they are.
Your doctor may order blood tests to determine the cause of your fibroids. Your complete blood count (CBC) can assist them in determining whether you have anaemia (low red blood cell counts) or other bleeding diseases.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)– If your doctor needs additional information following an ultrasound, you may be subjected to an MRI. MRIs provide more comprehensive images of fibroids and can assist doctors in determining the best treatment. If you have a big uterus or are nearing menopause, your doctor may also recommend an MRI.
Hysterosonography – In this examination, a specialist injects saline into your uterine cavity to dilate it. This allows them to see fibroids that are growing into your uterus (submucosal fibroids) as well as the uterine lining. This is beneficial if you are attempting to conceive or have heavy periods.
Hysterosalpingography – A hysterosalpingography may be performed if your doctor needs to determine whether your fallopian tubes are blocked. To help see your uterus and fallopian tubes better on an X-ray, your doctor will apply dye to highlight these areas.
Hysteroscopy – Your doctor puts a small telescope equipped with a light into your cervix. They can next examine the walls of your uterus and the fallopian tube opening after injecting saline and widening your uterine chamber.
Treatment for Uterine Fibroids
Fibroids can be treated in a variety of methods. The treatment that is best for you will be determined by whether you are experiencing symptoms, whether you wish to become pregnant, your age, and the location of your fibroids.
Waiting with caution: If you just experience minor symptoms – or none at all – your doctor may advise you to simply wait and see. Fibroids do not always cause cancer, and grow slowly or not at all. They may also shrink or disappear after menopause.
Medications: Fibroid medications alleviate your problems. Fibroids will not disappear; however, they may diminish with some treatments. Medication can also assist with symptoms such as discomfort and bleeding.
Oral contraception can help to minimise bleeding. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help relieve discomfort. If you have anaemia as a result of heavy bleeding, vitamins and iron supplements can aid with energy.
Oriahnn is the first FDA-approved non-surgical, oral drug alternative for the control of severe menstrual bleeding. It is a combination of elagolix (a GnRH antagonist), oestrogen, and progestin. Taking the medicine can lower the bleeding by 50% on average.
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists that cause menopause by inhibiting oestrogen and progesterone. This may cause your fibroids to shrink. This option may be selected by your doctor before surgery.
Heavy bleeding can be controlled using a progestin-releasing intrauterine device (IUD) which is put into your uterus. It also helps to avoid pregnancy.
Tranexamic acid (Cyklokapron, Lysteda) is a drug that does not contain hormones. You take it on days when you’re bleeding a lot to slow down the flow.
Surgery. If your symptoms are moderate or severe, surgery may be required to alleviate them. Among the options are:
Myomectomy: This procedure removes fibroids while attempting to leave healthy tissue alone. If you want to become pregnant in the future, this may be your best option. A myomectomy can be performed in a variety of techniques, ranging from major abdominal surgery to laparoscopy.
Ablation of the endometrium: To remove or destroy the lining of your uterus, a surgeon may use a laser, wire loops, hot water, electric current, microwaves, or freezing. This small surgery may be performed as an outpatient procedure. Typically, you will no longer be able to get pregnant after it, and you will no longer be able to have periods.
Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE): Also known as uterine artery embolization (UAE), is a type of embolization that occurs in the uterus (UAE). A doctor uses this treatment to stop the flow of blood to your fibroids by putting gel or plastic particles into adjacent blood vessels. This causes the fibroids to contract.
Hysterectomy: This operation fully eliminates your uterus. This is the only approach to eliminate fibroids. It’s a significant surgery but your doctor has choices, such as cutting through the abdomen or performing a laparoscopy. Book your appointment for fibroid treatment at Dr Amita Shah’s Global Women’s Clinic.