If you experience severe pain during your periods, similar to labour pains, and suffer from heavy bleeding with large blood clots, you might have adenomyosis.
This medical condition can cause adenomyosis bulky uterus, where the uterine tissue grows excessively into the muscular wall of the uterus.
Today, I will explain what adenomyosis is, why it occurs, its symptoms, and its treatments. I am Dr. Amita Shah, a Senior Consultant Gynaecologist and Laparoscopic Surgeon practising in Gurgaon.
What is Adenomyosis in Uterus?

Adenomyosis in uterus is a condition where the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows into the muscular wall of the uterus (myometrium), causing the uterus to become enlarged and bulky.
This abnormal tissue growth can lead to severe menstrual pain, heavy bleeding, and other symptoms.
It commonly affects women between the ages of 35 and 50 and is becoming more prevalent.
What Causes Adenomyosis?
The Adenomyosis in uterus has three layers: the outer wall, which we call the serosa; the inner lining, which is known as the endometrium; and the middle layer, which we call the myometrium, or the muscular wall.
Every month, the endometrium, which is the inner layer of the uterus, gradually grows. If pregnancy does not occur, this tissue sheds during menstruation.
However, in some cases, the endometrial cells begin to grow into the myometrium. Essentially, there is an invasion of these cells into the myometrium.
The basic nature of these cells is that they will grow each month and shed as part of menstruation.
But if bleeding occurs in these cells within the myometrium every month, there is no way for the blood to exit the body. Gradually, this blood accumulates, leading to the condition known as adenomyosis.
As a result, the uterus gradually enlarges due to blood accumulation. This enlarged uterus is known as a bulky uterus or adenomyotic uterus.
When these cells spread throughout the entire myometrium of the uterus, it is called diffuse adenomyosis. However, in some cases, they may accumulate in just one area and form a lump, which is referred to as localized adenomyosis.
Symptoms of Adenomyosis
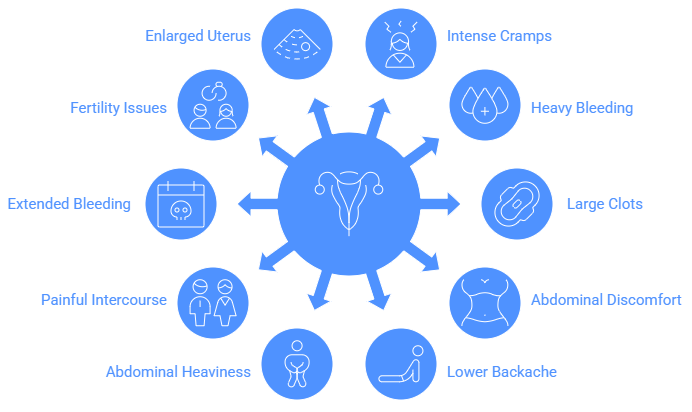
The primary symptom of adenomyosis in the uterus is severe pain during menstruation. Many women describe this pain as being similar to labour pains.
This type of pain is known as congestive dysmenorrhea. It typically starts one or two days before your period begins and gradually worsens, continuing until the end of the period.
In some cases, women may experience a constant dull aching pain throughout the month. This medical condition can also cause lower back pain.
As the uterus becomes heavy and bulky, women may feel a heavy sensation in the lower abdomen. Pain may also occur during intercourse.
Periods can become very heavy, with some women experiencing prolonged bleeding for 10 to 15 days. Large blood clots may also be present. In some cases, adenomyosis can cause infertility.
It is rare, but sometimes adenomyosis shows no symptoms. In such cases, an ultrasound may reveal an enlarged or adenomyotic uterus.
Adenomyosis symptoms:
- Intense Cramps – Severe menstrual pain like labour.
- Heavy Bleeding – Excessive blood flow during periods.
- Large Clots – Notable large blood clots in discharge.
- Abdominal Discomfort – Persistent lower abdominal pain.
- Lower Backache – Ongoing lower back pain.
- Abdominal Heaviness – Feeling of fullness in the lower abdomen.
- Painful Intercourse
- Extended Bleeding – Menstrual bleeding lasting up to 15 days.
- Fertility Issues – Possible difficulty conceiving.
- Enlarged Uterus – The uterus may be enlarged, often found via imaging.
How is Adenomyosis Diagnosed?

The diagnosis of adenomyosis in uterus usually begins with the evaluation of symptoms. Based on these symptoms, adenomyosis may be suspected and an ultrasound might be recommended. The diagnosis is confirmed through the ultrasound.
During the ultrasound, signs of blood accumulation or cysts in the myometrium, the muscular layer of the uterus, are looked for.
The presence of these abnormalities confirms the diagnosis of adenomyosis in the uterus.
Diagnosis options for Adenomyosis in Uterus:
- Ultrasound
Imaging Test: Detects uterine abnormalities and blood accumulation through sound waves.
- MRI
Detailed Scan: Provides high-resolution images of uterine tissue for confirmation of adenomyosis.
- Biopsy
Tissue Sample: Analyses a sample of uterine lining to rule out other conditions and confirm adenomyosis.
- Hysteroscopy
Direct Visualization: Uses a lighted tube to view the inside of the uterus and identify abnormalities.
- Symptom Assessment
Clinical Review: Evaluates symptoms like severe pain and heavy bleeding to guide diagnosis.
What is the Treatment for Adenomyosis?

The management of adenomyosis treatment involves a strategic approach to alleviate symptoms and enhance patient well-being.
Treatment options are primarily categorized into medical management, which focuses on regulating symptoms and hormonal imbalances, and surgical interventions, considered for more advanced cases or when medical therapy proves inadequate.
There are two main treatment options for adenomyosis: medical treatment and surgical treatment.
Medical Treatment for adenomyosis in uterus Medical treatment for adenomyosis involves managing the condition by regulating the menstrual cycle.
Since adenomyosis worsens with each cycle due to bleeding from endometrial cells, adenomyosis treatment often includes medications that reduce or halt menstrual bleeding to alleviate symptoms and control the progression of the disease.
Medication options for adenomyosis in uterus include:
- Oral contraceptive pills: These need to be taken continuously every month without breaks
- Progestin-only pills: For example, Dienogest. These pills are another option to manage adenomyosis symptoms.
- Mirena: A newer option, Mirena is an intrauterine device (IUD) similar to a copper IUD. It releases a small amount of progestin daily, which helps dry out the endometrium. This often reduces or even stops periods in 70-80% of cases.
If adenomyosis is diagnosed early, medical treatment alone may be sufficient. Surgical Treatment for Adenomyosis in uterus Surgical treatment for adenomyosis involves addressing more severe cases or when medical therapy is inadequate.
Adenomyosis treatment options include procedures to remove the affected areas of the uterus while preserving its function, or a hysterectomy for comprehensive resolution in advanced cases, aiming to significantly alleviate symptoms and enhance quality of life.
Surgical options for adenomyosis in uterus include:
- Adenomyomectomy: Removing the adenomyosis-affected area while preserving the uterus.
- Hysterectomy: Removing the uterus, which is considered if the patient is between 45-50 years old, has completed their family, and has diffuse adenomyosis.
What to Do if You Have Severe Adenomyosis Symptoms
If you’re dealing with severe pain or heavy bleeding, it’s important to see a doctor right away, as these symptoms might be due to adenomyosis.
Early diagnosis can lead to effective management with adenomyosis treatment, and in many cases, medical intervention alone can provide significant relief.







