Bulky Uterus Treatment & Pain Relief
Do you experience severe pain during periods, similar to labour pain?
Do you have very heavy bleeding with large blood clots?
If yes, you may be suffering from a condition called Adenomyosis. we will explain:
- What is adenomyosis
- Why it occurs
- Its symptoms
- Available treatment options
What Is Adenomyosis?
I am Dr. Amita Shah, Senior Consultant Gynecologist and Laparoscopic Surgeon practicing in Gurgaon.
Adenomyosis is a condition of the uterus in which the uterus becomes enlarged, heavy, or bulky. It is most commonly seen in women between the ages of 35 and 50 years and has become increasingly common in recent years.
Why Does Adenomyosis Occur?
The uterus has three layers:
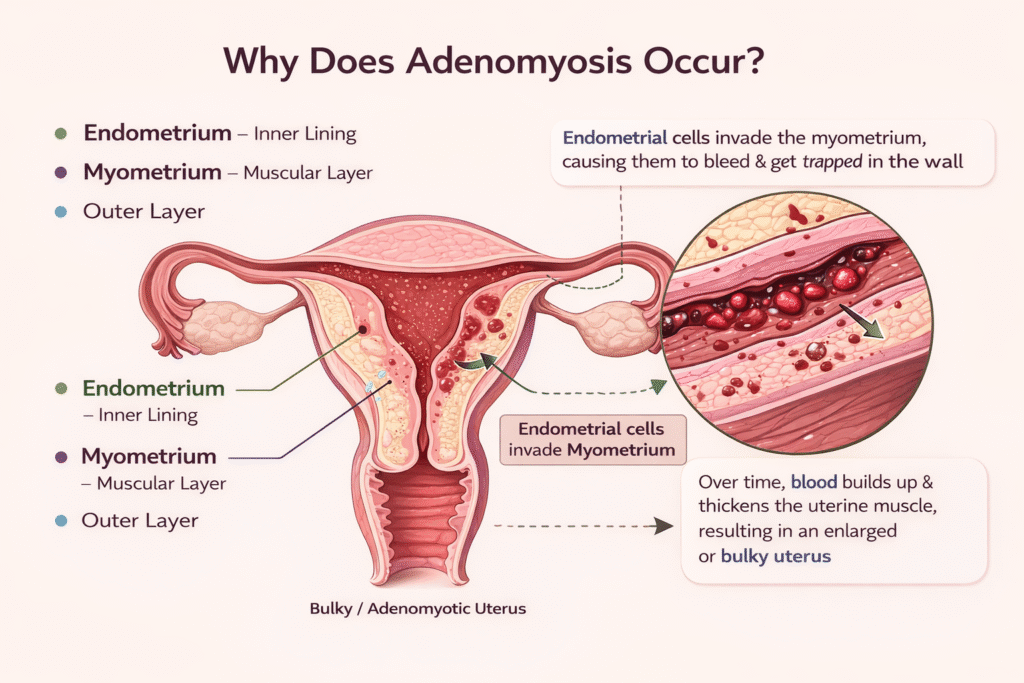
- Endometrium – the inner lining of the uterus
- Myometrium – the muscular layer of the uterus
- Outer layer – the outer covering
Every month, the endometrium thickens in preparation for pregnancy. If pregnancy does not occur, this lining sheds as menstrual bleeding.
In adenomyosis, endometrial cells grow into the myometrium (muscle layer). These cells continue to behave like normal endometrial tissue, meaning they bleed every month. However, since the blood has no way to exit, it becomes trapped within the muscle layer.
Over time, blood accumulation causes thickening of the uterine muscles, leading to an enlarged or bulky uterus, also known as an adenomyotic uterus.
Types of Adenomyosis

- Diffuse Adenomyosis
– When adenomyosis spreads throughout the uterine muscle
- Localized Adenomyosis (Adenomyoma)
– When adenomyosis forms a localized mass or knot in one area
Symptoms of Adenomyosis
Common symptoms include:
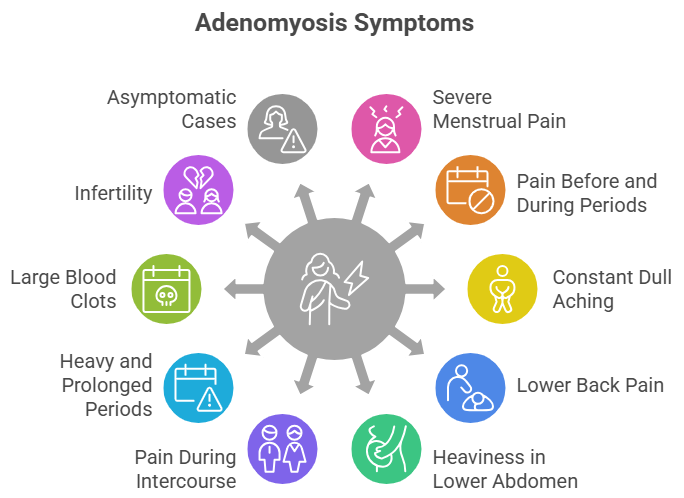
- Severe menstrual pain, often described as labour-like pain
- Pain starting 1–2 days before periods and lasting until bleeding ends
- Constant dull aching pain throughout the month
- Lower back pain
- Feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Heavy and prolonged periods lasting 10–15 days
- Passage of large blood clots
- Infertility in some cases
In rare cases, women may have no symptoms, and adenomyosis is detected incidentally on ultrasound.
How Is Adenomyosis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis is based on:
- A detailed evaluation of symptoms
- Ultrasound examination, which shows changes and blood collections within the uterine muscle layer
Ultrasound helps confirm the presence of a bulky or adenomyotic uterus.
Treatment Options for Bulky Uterus (Adenomyosis)
Treatment depends on age, symptoms, and fertility plans. There are two main approaches:
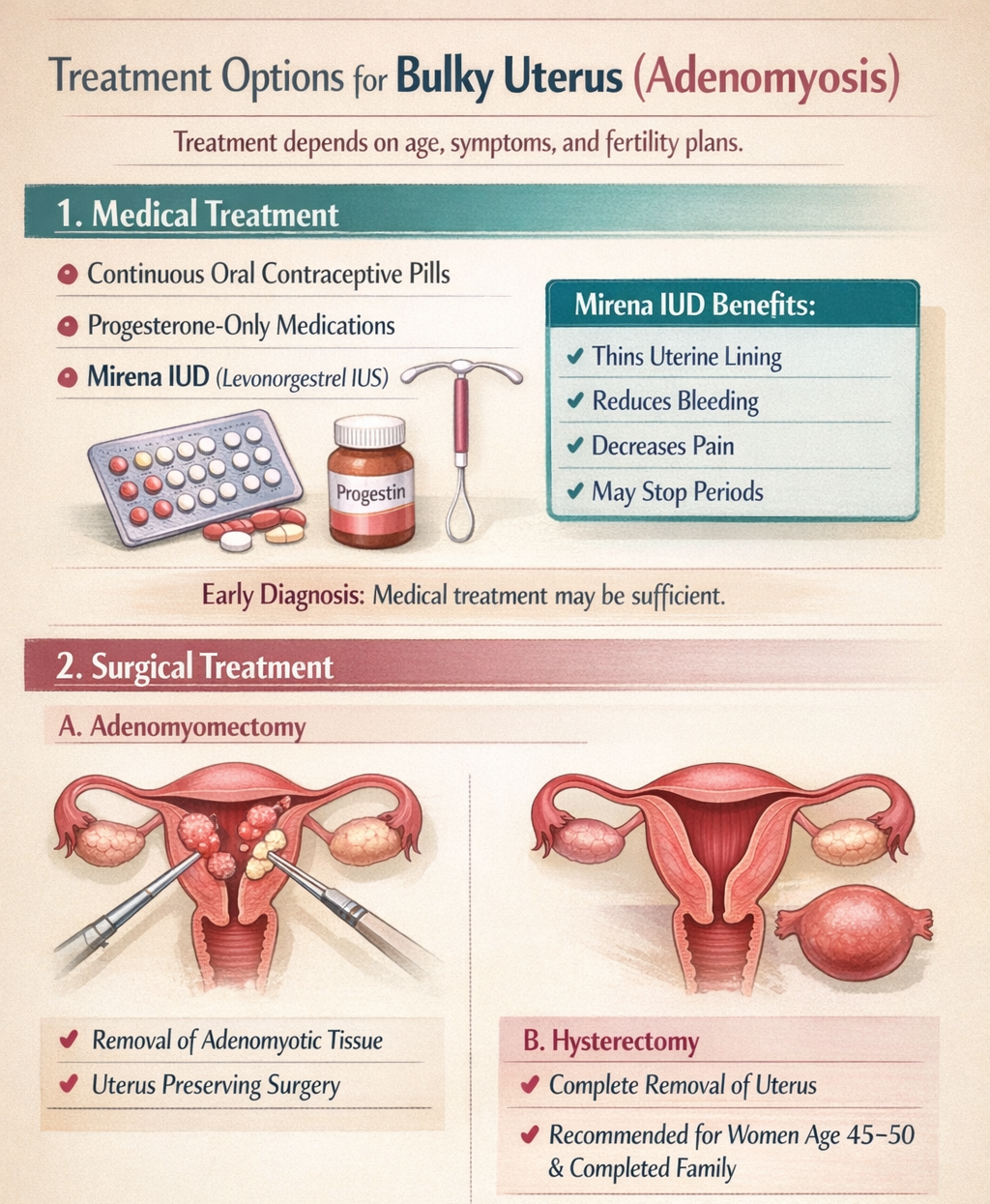
1. Medical Treatment
Adenomyosis worsens due to monthly menstrual cycles. By reducing or stopping periods, disease progression can be controlled and symptoms relieved.
Medical treatment options include:
- Continuous oral contraceptive pills
- Progesterone-only medications (such as Dienogest)
- Mirena (Levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system)
Mirena is a hormone-releasing intrauterine device that gradually releases progesterone, which:
- Thins the uterine lining
- Reduces menstrual bleeding
- Decreases pain in 70–80% of patients
- May completely stop periods in some women
If adenomyosis is diagnosed early, medical treatment alone may be sufficient.
2. Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered when symptoms are severe or unresponsive to medication.
A. Adenomyomectomy
- Surgical removal of adenomyotic tissue
- Preferred for women who wish to preserve the uterus or plan future pregnancy
- Complete removal of the uterus
- Recommended for women aged 45–50 years, with completed family and diffuse adenomyosis
When Should You See a Doctor?
If you experience:
- Severe menstrual pain
- Excessive or prolonged bleeding
- Passage of large blood clots
You should consult a gynecologist immediately.
Early diagnosis can help manage adenomyosis effectively and may prevent the need for surgery.





